CFI Group is pleased to present the Specialty Chemicals Valuation Snapshot for the first semester 2025. This report provides commentary and analysis on current market trends and M&A activity within the Specialty Chemicals sector.
Spotlight
The first half of 2025 has been difficult for Europe’s chemical industry. Output fell by over 2%, utilisation rates stayed well below average, and high gas prices — almost three times US levels — continued to erode competitiveness. Weak demand from automotive and construction sectors, combined with faster-growing imports, cut the region’s trade surplus sharply. Without relief on energy costs or stronger downstream recovery, Europe risks losing further ground globally.
India, by contrast, remained resilient. Strong domestic demand and rising exports in specialties kept growth intact, supported by government policy and new capacity additions. Indian producers are moving up the value chain and benefiting from global buyers diversifying supply chains away from China.
The US sector stayed stable, supported by low-cost shale gas and steady demand from industrial and consumer markets. Abundant feedstock supply helped keep utilisation high and costs competitive, reinforcing its structural advantage over Europe.
China led global growth, with chemical output up nearly 8% in H1. Government support, recovering manufacturing demand, and strong performance in electronics, batteries, and infrastructure-related segments kept momentum high, even as challenges in real estate lingered.
Globally, chemical production still grew by around 4% in H1 2025, but growth was concentrated in Asia and the US, while Europe lagged. The divergence between cost-advantaged and cost-pressured regions is becoming more pronounced.
Global Outlook
M&A activity reflects this shift. Deal volumes have declined, but average deal size is up, with companies pursuing fewer but more strategic moves. The focus is on “divest-to-invest” strategies, freeing resources for specialties, advanced materials, and sustainable technologies. Asia has been the most active region for such deals, while Europe remains subdued. Going forward, value creation will hinge less on scale and more on sharper portfolios, operational discipline, and positioning in high-growth, innovation-led markets.
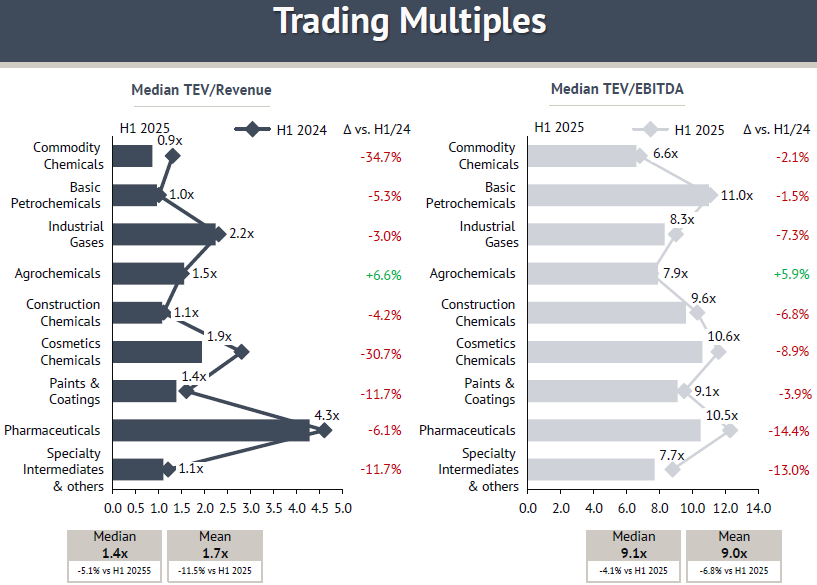
H1/25, trading multiples in the chemicals sector declined, reflecting weaker investor sentiment driven by slower global growth, renewed U.S. tariffs, and geopolitical uncertainty. With U.S.-listed companies making up a substantial portion of the dataset, the reported valuation trends are particularly sensitive to American policy shifts and investor sentiment. The median TEV/Revenue fell to 1.4x (-5.1% YoY), while the median TEV/EBITDA dropped to 9.1x (-4.4% YoY). This signals that equity markets are pricing in lower growth and profitability expectations across much of the industry.
The sharpest repricing occurred in Commodity Chemicals, where TEV/Revenue multiples fell from 1.4x to 0.9x (-34.7% YoY). This shows that investors are assigning very limited value to sales in a segment heavily exposed to cyclical swings and international trade flows. Cosmetics also performed poorly, with TEV/Revenue multiples falling -30.7% YoY and TEV/EBITDA down -8.9% YoY, highlighting the impact of weak consumer demand. In contrast, Agrochemicals was the only subsector to post gains, with TEV/Revenue up +6.6% and TEV/EBITDA up +5.9% YoY, supported by resilient food demand and defensive business models.
Pharmaceuticals, which previously led sector valuations, corrected as well. TEV/Revenue declined -6.1% YoY, while TEV/EBITDA fell -14.4% YoY, suggesting a normalization after several strong quarters. Industrial Gases posted more modest declines, with TEV/Revenue down -3.0% YoY and TEV/EBITDA down -7.3% YoY.
The drop indicates that, despite supportive long-term demand in energy and industrial end-markets, near-term pricing pressure has begun to weigh on investor expectations. Basic Petrochemicals (-5.3% in TEV/Revenue) similarly showed signs of valuation pressure.
Construction Chemicals and Specialty Intermediates also reported declines across both valuation metrics, pointing to weaker building activity and softer demand in industrial supply chains. These results underline that the pressure on trading multiples is broad-based, sparing only a few of more resilient subsectors.
Looking ahead, the sector faces a challenging environment. The new U.S. tariffs on imports, particularly from Europe, are disrupting global trade flows and creating uncertainty in investment planning, especially due to the chemical heavy-weights sitting in DACH-Area. Combined with softer macroeconomic indicators and the risk of recession in key markets, these factors weigh on profitability expectations. Still, subsectors with stable or counter-cyclical demand, such as Agrochemicals, are expected to remain more resilient. Overall, the sector has underperformed, with valuations remaining under pressure. A recovery could emerge once companies and investors adapt to new tariff structures and recession fears ease, provided geopolitical uncertainties are gradually resolved.
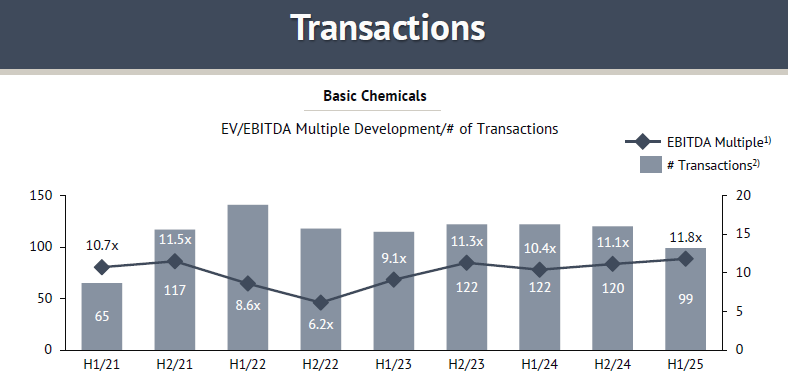
In H1/25, M&A activity in Basic Chemicals slowed further, with 99 announced transactions, down from 120 in H2/24 and well below the H1/22 peak of 141. By contrast, valuations strengthened: the median disclosed EV/EBITDA multiple rose to 11.8x, the highest level observed across the last nine semesters and above the 11.1x recorded in H2/24.
This divergence underscores the selectivity of current market dynamics. While overall deal volumes remain under pressure, competitive tension for resilient and strategically relevant businesses continues to drive disclosed multiples higher. The sharp rebound from the 6.2x trough in H2/22 illustrates the volatility of a small disclosure base, yet the consistent return to double-digit levels since 2023 indicates that investor appetite for quality assets has not structurally weakened.
At the same time, the sector remains exposed to persistent structural headwinds. Regulatory requirements, rising input costs, and trade frictions – particularly U.S. tariffs – are compressing margins and weighing on broader market sentiment. Against this backdrop, H1/25 highlights a disciplined M&A environment, where buyers are cautious on volume but willing to pay a premium for differentiated Basic Chemicals platform.
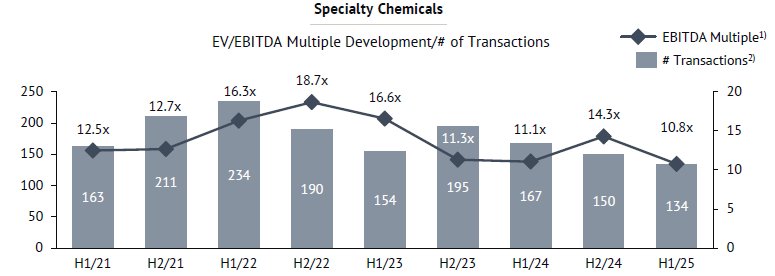
In H1/25, median EV/EBITDA multiples in the Specialty Chemicals sector declined, marking a sharper correction compared to the relative stability observed in 2024. With 134 deals announced, activity remained lower versus H2/24. The median multiple decreased to 10.8x, the lowest level since 2021, pointing to a more cautious valuation environment.
The decline reflects an easing of the momentum that had gradually returned in 2024, as financial sponsors continue to reassess pricing discipline amid broader market uncertainties. Nevertheless, private equity remains a key driver of activity, supported by ample dry powder and continued appetite for add-on acquisitions. While premiums for high-quality assets persist, the narrowing of headline multiples suggests that investors are focusing on operational resilience and profitability rather than paying for growth alone.
Looking ahead, the role of financial investors in shaping deal activity is expected to remain significant, though with greater selectivity. This shift could further accentuate the polarization of valuations between best-in-class Specialty Chemicals businesses and more commoditized assets.
Global Deal Activity – Overview
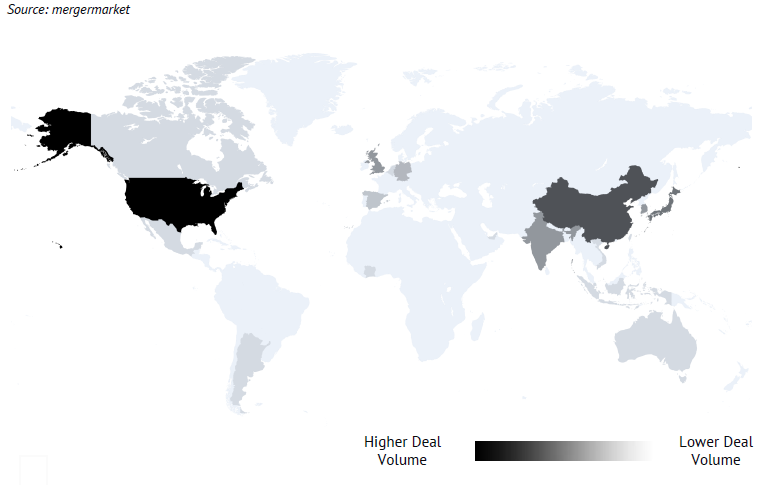
In the global M&A landscape across specialty and basic chemicals, deal activity in H1 2025 was led by the United States, which recorded the highest volume of transactions. A favorable cost environment, strong capital availability, and steady demand across industrial and specialty markets reinforced its position as the most active hub. Private equity participation remained significant, and portfolio reshaping continued to drive deal flow.
China and India followed as key centers of activity. China benefitted from strong industrial demand, government support, and ongoing interest in high-value segments such as advanced materials and sustainability-linked solutions. India maintained resilience through strong domestic consumption and rising interest from global buyers seeking diversification and access to its fast-growing market.
South Korea, Japan, and Southeast Asia registered moderate activity, largely in technology-driven and specialty segments, reflecting the region’s focus on innovation and advanced materials.
Europe showed more restrained deal-making. While Germany, Italy, and the UK remain relevant players, high energy costs, regulatory complexity, and subdued demand weighed on overall volumes. Transactions were concentrated in selective niches rather than broad-based consolidation.
Latin America remained lighter in volume, with Brazil and Mexico leading regional transactions, particularly in agrochemicals and industrial applications. The Middle East and Africa featured smaller but notable deals, with the UAE consolidating its role as a cross-regional hub and South Africa contributing resource-linked activity.
Overall, the United States emerged as the clear leader in global chemical M&A by volume, with China and India as the next most active markets. Europe stayed subdued, while Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa presented selective, sector-specific opportunities.